No. 4.7.5
Surface Mount, BGA Pad with Integral Via Repair Circuit Extension Method
OUTLINE
This method is used to replace damaged BGA pads with new dry film adhesive
backed pads. The new pads are bonded to the circuit board surface using a specially
designed bonding press or bonding iron. Electrical connection is made to a via
circuit which is originally manufactured integral to the pads.
NOTE
This method uses replacement BGA pads. The new pads are fabricated from copper foil. They are available in a
variety of sizes and shapes and are generally supplied solder plated. If a special size or shape is needed
they can be custom fabricated.
TOOLS & MATERIALS
Ball Mills
Bonding Iron
Bonding Tips
Bonding System
Circuit Frames, BGA Pads
Cleaner
Epoxy
Flux, Liquid
Knife
Micro-Drill System
Micro Pad Repair Kit
Microscope
Oven
Scraper
Solder
Soldering Iron
Tape, Kapton
Tweezers
Wipes
PROCEDURE
NOTE
Prior to proceeding determine whether this procedure or C4-7-4 Surface Mount, BGA Pad with Integral
Via Repair, is the appropriate method. This method is best used when a connecting circuit or plane clearly
runs from the integral via and is close to the board’s affected surface to permit exposure of the circuit
for the repair connection.
- Clean the area.
- Carefully remove the defective pad to avoid damaging the integral via (See Figure 1).
- Use a knife and scrape off any epoxy residue, contamination or burned material from the board surface.
- Using a Micro-Drill system (See Figure 2) and the appropriate ball mill down to the connecting circuit,
exposing the copper surface of the etch (See Figure 3). Be careful not to cut through the circuit.
- Clean the area
- Apply a small amount of liquid flux to the circuit connection now exposed beneath the surface of the
board. Tin the circuit with solder (See Figure 4 ). Clean the area.
- In general, the area for the new pad on the board surface must be smooth and flat. If internal fibers
of the board are exposed, or if there are deep scratches in the surface, they should be repaired. Refer to
appropriate procedure.
- Select a replacement BGA pad that most closely matches the surface mount pad to be replaced. If a special
size or shape is needed they can be custom fabricated. (See Figure 5). Ensure the selected pads attached
circuit matches the width and thickness of the circuit to be replaced. Trim the width approximately as needed. The circuit should overlap the existing
circuit a minimum of 2 times the circuit width.
NOTE
New BGA pads are fabricated from copper foil. The foil is plated on the top side with solder, and an
adhesive bonding film is applied to the bottom side.
- Before trimming out the new pad, carefully scrape off the adhesive bonding film from the solder joint
connection area on the back of the replacement circuit portion of the new pad. In order to ensure
that the final pressed pad lays flat (and the new circuit is properly connected to the exposed board
circuit), it may be necessary to remove the film from the whole length of the connecting circuit up to
the pad itself. (See Figure 6).
CAUTION
When handling the replacement pad, avoid
touching the epoxy backing with your fingers or other materials that may
contaminate the surface and reduce the bond strength.
-
Cut out and trim the new pad. Cut out from the plated side.
-
Place the pad on the board so that the connecting circuit can be fit into the
trough containing the board’s tinned circuit (See Figure 7).
-
Select a bonding tip with a shape to match the shape of the new pad. See bonding
tip chart in the replacement parts section of the manual provided with the repair system or repair kit.
(See Figure 8).
NOTE
The tip used for bonding should be as small as possible but should completely
cover the entire surface of the new pad.
- Position the circuit board so that it is flat and stable. Gently place the bonding tip
directly onto the new pad. Apply pressure as recommended in the manual of the repair system
or repair kit for 30 seconds to fully bond the pad. The new pad is fully cured. Carefully
clean the area and inspect the new pad for proper alignment
CAUTION
Excessive bonding pressure may cause measling in the circuit board surface or
may cause the new pad to slide out of position.
-
Apply flux to the overlapping connecting circuit in the bottom of the trough.
Solder in place. Clean the area
NOTE
The circuit board may be preheated prior to filling the area with epoxy. A preheated circuit board
will allow the epoxy to easily flow and level out. Epoxy applied to an unheated circuit board may settle below
the circuit board surface as the epoxy cures.
-
Mix epoxy. If desired, add color agent to the
mixed epoxy to match the circuit board color.
-
Coat the top and sides of the replaced circuit with epoxy. The epoxy bonds the new
circuit to the base board material and insulates the circuit. Continue adding epoxy up to the top surface
of the circuit board.
NOTE
A very slight overfill of epoxy may be desired
to allow for shrinkage when the epoxy cures. Additionally, in order to allow the
circuits appearance to match the board, it may be necessary to mask the circuit
prior to filling the excavated area.
- Cure the epoxy per Procedure 2.7 Epoxy Mixing and Handling
CAUTION
Some components may be sensitive to high temperature.
- Additional epoxy can be applied around the perimeter of the new pad to provide additional bond
strength. Mix epoxy. Cure the epoxy per Procedure 2.7 Epoxy Mixing and Handling. Use the maximum
recommended heat cycle to ensure the highest strength bond. BGA pads are routinely subjected to one or
more reflow cycles.
CAUTION
Some components may be sensitive to high temperature.
- Apply surface coating to match prior coating as required. (See Figure 9)
EVALUATION
- Visual examination.
- Measurement of new pad width and spacing.
- Electrical continuity measurement.
|
|
|
Solutions Across the Board
TM
|
|
|
|
Product Class: R/F/C
Skill Level: Expert
Conformance Level: High
Revision: B
Revision Date: May 8, 2001
Repair Service Charge
 Figure 1: Remove the damaged pad with integral via.
Figure 1: Remove the damaged pad with integral via.

Figure 2: Micro-Drill System and ball mills.
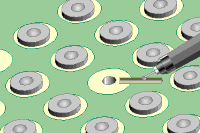
Figure 3: Using a Micro-Drill expose the copper circuit by recessing a trough or gully.
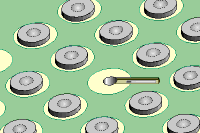 Figure 4: Tin the circuit with solder.
Figure 4: Tin the circuit with solder.
 Figure 5: Select a replacement pad that matches the missing pad.
Figure 5: Select a replacement pad that matches the missing pad.
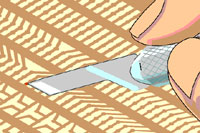 Figure 6: Scrape off the adhesive bonding film from the solder joint connection area on the back of new pad.
Figure 6: Scrape off the adhesive bonding film from the solder joint connection area on the back of new pad.
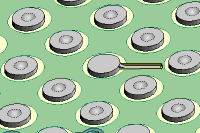 Figure 7: Connecting circuit connected to the exposed and tinned circuit.
Figure 7: Connecting circuit connected to the exposed and tinned circuit.
 Figure 8: Bond the new pad using a Bonding
System.
Figure 8: Bond the new pad using a Bonding
System.
 Figure 9: Completed repair.
Figure 9: Completed repair.
|
|
|


 Figure 1: Remove the damaged pad with integral via.
Figure 1: Remove the damaged pad with integral via.


 Figure 4: Tin the circuit with solder.
Figure 4: Tin the circuit with solder.
 Figure 5: Select a replacement pad that matches the missing pad.
Figure 5: Select a replacement pad that matches the missing pad.
 Figure 6: Scrape off the adhesive bonding film from the solder joint connection area on the back of new pad.
Figure 6: Scrape off the adhesive bonding film from the solder joint connection area on the back of new pad.
 Figure 7: Connecting circuit connected to the exposed and tinned circuit.
Figure 7: Connecting circuit connected to the exposed and tinned circuit.
 Figure 8: Bond the new pad using a
Figure 8: Bond the new pad using a  Figure 9: Completed repair.
Figure 9: Completed repair.