No. 4.6.3
Edge Contact Repair/Rework, Plating Method
OUTLINE
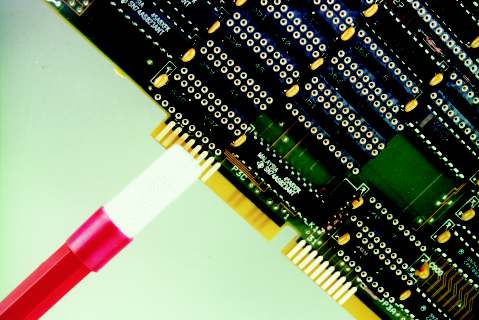
This method is used to replate edge contacts by selective swab plating. Edge
contacts may require replating if they become contaminated with solder or are
scratched during handling. Other applications may arise when the plating on the
edge contacts does not meet the minimum thickness specification or if the
specification changes.
This electroplating process uses a DC power supply. One lead is connected to
the connector edge contacts that need plating. A second lead is connected to the
plating probe. The plating probe has an anode fastened to the tip. The anode has
absorbent wrapping. The anode is dipped into high-speed proprietary plating
solutions. When the saturated anode is swabbed across the circuit board connector
edge contacts, the metal contained in the solution is plated wherever electrical
contact is made. Prior to replating any solder contamination must be removed.
CAUTION
This method can be used to replate any metal surface including connector edge
contacts, but it is essential that the surface to be plated is free of deep
scratches, nicks, pin holes or other defects. If the edge contacts need to be
replaced see appropriate procedure.
SAFETY
A thorough review of this method should be made before repairs are attempted.
Technicians should become familiar with the tools included and should practice
on scrap circuit boards.
To expect the best results a clean work environment is essential. A smooth
work surface and good lighting are recommended. Safety glasses and safety gloves
should always be worn when handling hazardous chemicals.
The work area should be adequately ventilated. It is particularly important
to have adequate ventilation when using gold solution, since gold solution
contains a very small percentage of free cyanide. If ventilation is not
adequate, use a fan to move fumes away from the operator.
CAUTION
It is essential to follow the manufacturer's instruction supplied with the
plating equipment.
| ACCEPTABILITY REFERENCES |
| IPC-A-600 |
2.0 |
Externally Observable Characteristics |
| IPC-A-610 |
10.0 |
Laminate Conditions |
| |
| PROCEDURE REFERENCE |
| CTC-7721 |
1.0 |
Foreword |
| CTC-7721 |
2.1 |
Handling Electronic Assemblies |
| CTC-7721 |
2.2 |
Cleaning |
| IPC-7721 |
4.6.3 |
Edge Contact Repair/Rework, Plating Method |
TOOLS & MATERIALS
Abrasive Pad
Board Support
Cleaner
Conductive Pen
Desoldering Braid or Desoldering System
Eraser Stick
Flux, Liquid
Gloves, Antistatic
Gold Contact Plating System
Knife
Peel Testing Tape
Pin Fixtures
Plating Anodes
Plating Solution, Gold
Plating Probes
Plating Solution, Electroclean
Plating Cables
Plating Solution, Nickel
Plating Solution, Solder Strip
Plating Tape
Power Supply
Probe Clip
Rinse Tray
Rinse Bottle
Safety Glasses
Soldering Iron
Solder
Solution Swab
Solution Cups
Solution Tray
Tape, Kapton
Thickness Measuring System, Gold and Nickel
Water Sprayer
Wipes
Wire, Bus, 30 AWG
Work Sink
PREPARATION - Remove Solder Contamination
CAUTION
Safety glasses and safety gloves should always be worn when handling hazardous
chemicals. Do not work within a small enclosed room without supplemental
ventilation. If ventilation is not adequate, use a fan to move fumes away from
the operator.
- Clean the rework area.
- Apply plating tape to the circuit board surface surrounding the area to be
reworked. The plating tape will protect adjacent components and the circuit board
surface from unwanted exposure to stripping and plating solutions.
- Flow solder over the entire area of any contacts that have contamination
using a soldering iron. This provides a more even surface when plating. Remove
the bulk of the solder contamination using desoldering tools or desoldering
braid. (See Figure 2).
- Clean the area.
- Place the circuit board on the board support so that the leading edge overhangs
the rinse tray.
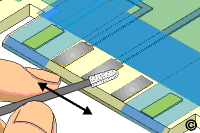
- Swab the solder stripping solution over the solder contamination using a
swab. Swab the surface until all remaining solder has been stripped off. (See
Figure 3).
- Thoroughly rinse the entire area with water. (See Figure 4).
- Mildly buff the contacts using abrasive pad. Mild buffing will prepare the
surface for plating and remove any remaining solder contamination.
- Thoroughly rinse with water to remove any residue.
PREPARATION - Remove Poor Plating or Surface Defects
- Clean the rework area.
- Apply plating tape to the circuit board surface surrounding the area to be
reworked. The plating tape will protect adjacent components and the circuit board
surface from unwanted exposure to stripping and plating solutions.
- Clean the area.
- Buff the contacts using an abrasive pad. Buff the contacts until all
defective or poor plating is removed.
- Burnish small scratches. Use the tip of the Tech-Pro Burnisher to work the
copper material into the scratch and smooth out the area. Finish by mildly
buffing the area to remove any minor burnishing marks. If there are large
scratches the contact may need replacement. See Procedure Number 4.6.1 or 4.6.2.
- Thoroughly rinse the entire area with water to remove any residue.
BUSING
A conductive bus must be made to all the contacts that need plating. There are 4
basic connection options.
NOTE
Making a reliable bus connection is the most important step in plating. All
sorts of problems will be eliminated by taking the time to make a reliable bus
connection.
BUSING - Wire Soldered to Edge (Option 1)
CAUTION
When finished, this method will leave a small unplated line along the inner tip
of each contact.
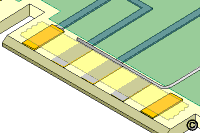
- Apply Kapton tape to all the contacts to be plated. The High
Temperature Tape should cover the entire contact except for a small line along
the inboard edge. The Kapton tape will prevent further solder
contamination.
- Solder a wire directly to the inboard tip or connecting circuit of each
contact to be plated. The smallest amount of solder should be used to prevent
further contamination. (See Figure 5).
BUSING - Conductive Paint Applied to Edge (Option 2)
CAUTION
When finished, this method will leave a small unplated line along the inner tip
of each contact.
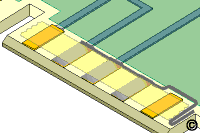
- Apply Kapton tape to all the contacts to be plated. The High
Temperature Tape should cover the entire contact except for a small line along
the inboard edge. The Kapton tape will prevent the conductive paint
from contaminating the contact surface.
- Apply a thin coating of conductive paint directly to the inboard tip of each
contact to be plated. The conductive paint should extend out to one edge so that
a clip can be applied to make electrical connection. (See Figure 6).
BUSING - Mechanical Probe, Individual Contacts (Option 3)
- Each contact needing plating can be individually probed using the plating
probe. Touch the tip of the plating probe to the inboard edge of each contact or
to the connecting circuit as each solution is applied during the plating
process.
BUSING - Pin Fixture, Multiple Contacts (Option 4)
- Make a mechanical connection to each contact using a pin fixture. The pin
fixture has spring loaded contact pins on centers matching the spacing of the
edge contacts to be plated. The contact pins make direct mechanical connection
to the inboard tip of each contact, the connecting circuit trace or a connecting
plated through hole..
PROCEDURE - Plating Process
- Place the circuit board on the board support so that the leading edge overhangs
the rinse tray.
- Make the cathode connection (-) to the circuit board by using a plating probe or
probe clip. Connect the probe clip directly to the wire bus connection or to the
edge where conductive paint has been applied. The cable should be connected to
the (-) or black jack on the power supply.
- Connect the plating probe to the power supply (+) or red jack. (See Figure
7).
- Set the output current on the power supply to setting recommended by the
equipment manufacturer. Refer to Table 1 for general voltage/time settings.
- Dip the plating probe into the electroclean plating solution. Wait a few
seconds for the solution to saturate the absorbent wrapping.
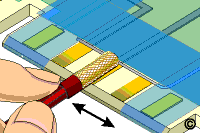
- Swab the entire surface to be plated by brushing the surface with the
saturated plating probe. The plating probe should be moved back and forth
briskly to prevent burning and to provide even coverage. (See Figure 8) Swab the
area for the time recommended by the equipment manufacturer. Refer to Table 1
for general voltage/time settings.
- Thoroughly rinse the entire area with water. Any burning or darkening of the
contacts may be removed with an abrasive pad. Saturate the abrasive pad and the
PC board surface with water and lightly buff the contacts until all evidence of
the burning or discoloring is removed. Rinse the entire area with water.
CAUTION
Do not allow the rework area to dry out between steps. The water coating
prevents oxidation.
- Connect the nickel plating probe to the power supply (+) or red jack.
- Set the output current on the power supply to setting recommended by the
equipment manufacturer. Refer to Table 1 for general voltage/time settings.
- Dip the plating probe into the nickel plating solution. Wait a few seconds
for the solution to saturate the absorbent wrapping.
- Swab the entire surface to be plated by brushing the surface with the
saturated plating probe. The plating probe should be moved back and forth
briskly to prevent burning and to provide even coverage. Swab the area for the
time recommended by the equipment manufacturer. Before rinsing, lightly buff the
contacts with an abrasive pad. Refer to Table 1 for general voltage/time
settings.
- Thoroughly rinse the entire area with water.
- Connect the gold plating probe to the power supply (+) or red jack.
- Set the output current on the power supply to setting recommended by the
equipment manufacturer. Refer to Table 1 for general voltage/time settings.
- Dip the plating probe into the gold plating solution. Wait a few seconds for
the solution to saturate the absorbent wrapping.
- Swab the entire surface to be plated by brushing the surface with the
saturated plating probe. The plating probe should be moved back and forth
briskly to prevent burning and to provide even coverage. Swab the area for the
time recommended by the equipment manufacturer. Refer to Table 1 for general
voltage/time settings.
- Thoroughly rinse the entire area with water.
- Remove and discard all plating tape and thoroughly rinse the area with
water. Dry the area using a water/air sprayer or wipes.
- Remove the wire or conductive paint used to bus the contacts.
CAUTION
Apply Kapton tape to protect the contacts from further contamination
while removing the bus connection.
- Thoroughly rinse the entire area with deionized water or rinse the circuit board
in an aqueous water cleaning system.
Table 1
Typical Voltage/Time Settings
| Surface Area
| Electroclean
| Nickel
| Gold
|
| Volts |
Time |
Volts |
Time |
Volts |
Time |
| <.01 in2 |
10.0 VDC |
5 sec. |
4.0 VDC |
10 sec. |
3.0 VDC |
10 sec. |
| .01 - .05 in2 |
10.0 VDC |
5 sec. |
4.0 VDC |
30 sec. |
3.5 VDC |
20 sec. |
| .05 - .10 in2 |
10.0 VDC |
5 sec. |
4.0 VDC |
1.0 min. |
4.0 VDC |
30 sec. |
| .10 - .20 in2 |
10.0 VDC |
10 sec. |
4.0 VDC |
2.0 min. |
4.0 VDC |
1.0 min. |
| .20 - .30 in2 |
10.0 VDC |
10 sec. |
4.0 VDC |
2.5 min. |
4.0 VDC |
1.5 min. |
| .30 - .40 in2 |
10.0 VDC |
10 sec. |
4.0 VDC |
3.0 min. |
4.0 VDC |
2.0 min. |
| .40 - .50 in2 |
10.0 VDC |
20 sec. |
4.0 VDC |
4.0 min. |
4.0 VDC |
2.5 min. |
| .50 - .60 in2 |
10.0 VDC |
20 sec. |
5.0 VDC |
5.0 min. |
4.0 VDC |
3.0 min. |
| .60 - .70 in2 |
10.0 VDC |
20 sec. |
6.0 VDC |
6.0 min. |
4.0 VDC |
3.5 min. |
| .70 - .80 in2 |
10.0 VDC |
30 sec. |
6.0 VDC |
7.0 min. |
4.0 VDC |
4.0 min. |
| .80 - .90 in2 |
10.0 VDC |
30 sec. |
6.0 VDC |
7.5 min. |
4.0 VDC |
4.5 min. |
| .90 - 1.00 in2 |
10.0 VDC |
30 sec. |
6.0 VDC |
8.0 min. |
4.0 VDC |
5.0 min. |
Notes:
- Surface Area is the total area being plated during each swab plating
operation.
- Voltage and Time setting shown in Table 1 are for a minimum of .000100"
Nickel and .000050" Gold.
- Settings are a guide. For precise thickness requirements the final thickness
should be verified with proper measuring equipment.
EVALUATION
- The rework area should be checked by measuring the thickness of the nickel
and gold to make sure they meet the minimum thickness requirement.
- The plating bond may also be checked by doing a peel test using peel testing
tape.
- Visually examine the rework area for color and luster.
|