No. 4.2.5
Conductor Repair, Through Board Wire Method
OUTLINE
This method is used on circuit boards to replace damaged or missing circuits on
the circuit board surface. A length of standard insulated or non insulated wire is
used to repair the damaged circuit.
CAUTION
The circuit widths, spacing and current carrying capacity must not be reduced
below allowable tolerances.
CAUTION
This method is not allowed when wire will be subsequently subjected to a mass
soldering operation.
TOOLS & MATERIALS
Cleaner
Flux, Liquid
Knife
Micro-Drill System
Microscope
Solder
Soldering Iron with Tips
Tape Dots
Wipes
Wire
Wire Guide
PROCEDURE
- Clean the area.
- Remove the damaged section of circuit using the knife. The damaged circuit
should be trimmed back to a point where the circuit still has a good bond to the
PC board surface.
NOTE
Heat can be applied to the damaged circuit using a soldering iron to allow the
circuit to be removed more easily.
- Use a knife and scrape off any solder mask or coating from the ends of the
remaining circuit. (See Figure 1).
- Remove all loose material. Clean the area.
- Apply a small amount of liquid flux to the ends of the remaining circuit.
Tin the exposed end of each circuit using solder and a soldering iron.
- Clean the area.
- Select a wire to match the width and thickness of the circuit to be
replaced. Cut a length approximately as needed. See Table 1 for Solid Wire
Equivalents.
Table 1 - Solid Wire Equivalents
| Conductor Width 2 oz. Copper |
Equivalent Solid Wire Diameter |
| .010" (0.25 mm) |
#34, .006" (0.15 mm) |
| .015" (0.38 mm) |
#32, .008" (0.20 mm) |
| .020" (0.50 mm) |
#31, .009" (0.23 mm) |
| .031" (0.78 mm) |
#29, .011" (0.28 mm) |
| .082" (2.08 mm) |
#26, .018" (0.46 mm) |
| .125" (3.18 mm) |
#23, .023" (0.58 mm) |
| When using solid wire to repair a conductor,
there should be no reduction in the cross sectional area. |
- Strip the wire and tin the ends if needed. Non insulated wire may be used
for short repairs if conductors are not crossed.
- Clean the wire.
- Drill through the board adjacent to both ends of the remaining circuits.
Drill the hole slightly larger than the wire diameter to be used. (See Figure
2).
CAUTION
Review circuit diagrams to be sure no surface or internal circuits will be
damaged or shorted.
- Position the wire on the opposite side from the repair and insert the
stripped ends into the drilled holes.
- Bend the stripped wire over the prepared circuits in line with the circuits.
The wire should overlap the existing circuit a minimum of 2 times the circuit
width. (See Figure 3).
NOTE
If the configuration permits, the overlap solder joint connection should be a
minimum of 3.00 mm (0.125") from the related termination. This gap will
minimize the possibility of simultaneous reflow during soldering operations.
Refer to 7.1 Soldering Basics.
- Apply a small amount of liquid flux to the overlap joint.
- Lap solder the wire to the circuits on the circuit board surface. Make sure the
wire is properly aligned. (See Figure 4).
- Form the wire on the opposite side to match the shape of the missing
circuit, if desired.
- Clean the area.
NOTE
It may be necessary to encapsulate the solder joint connection if electrical
spacing is reduced.
- If desired bond the wire to the circuit board surface with adhesive, epoxy or
Tape Dots. Refer to Section 6.0.
CAUTION
Some components may be sensitive to high temperature.
- Cure the epoxy per Procedure 2.7 Epoxy Mixing and Handling
- After the epoxy has cured clean the area.
EVALUATION
- Visual examination for alignment and overlap of wire.
- Electrical tests as applicable.
|
|
|
Solutions Across the Board
TM
|
|
|
|
Product Class: R
Skill Level: Advanced
Conformance Level: Meduim
Revision: D
Revision Date: Jul 7, 2000
Repair Service Charge
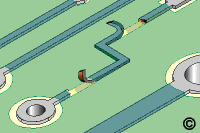
Damaged Conductor

Figure 1: Scrape off any solder mask or coating from the ends of the remaining
circuits
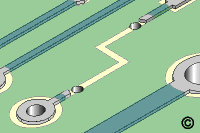
Figure 2: Drill through the board adjacent to both ends of the remaining
circuits.
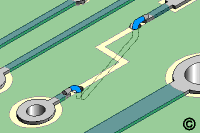
Figure 3: Bend the stripped wire over the prepared circuits in line with the
circuits.
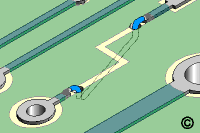
Figure 4: Lap solder the wire to the circuits on the circuit board surface.
|
|
|






